Boarding School: A Legacy of Learning and Life Beyond the Classroom
Introduction
For centuries, boarding schools have represented a unique educational experience that blends academic rigor with immersive life skills. Unlike day schools where students return home each evening, boarding schools offer a 24/7 learning environment, shaping not only the intellect but also the character of their students. Though often associated with elite education and tradition, modern boarding schools come in many forms—serving diverse populations across the globe with specialized programs and contemporary approaches to teaching.
This article explores the history, types, benefits, structure, challenges, and future of boarding schools, offering a comprehensive understanding of this enduring educational model.
What is a Boarding School?
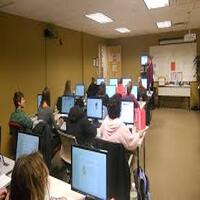
A boarding school is an educational institution where students live on campus during the school term. Students eat, sleep, study, and engage in recreational activities within the school premises, under the guidance of house parents, dorm supervisors, and faculty.
Boarding schools typically provide:
- Academic instruction
- Dormitory housing
- Meal services
- Extracurricular activities
- Structured daily routines
- Moral and personal development programs
A Brief History of Boarding Schools
Origins in Antiquity
Boarding schools can be traced back to ancient Greece and Rome, where noble families sent their sons to live and study under philosophers and scholars. In medieval Europe, monastic schools trained young men for religious and administrative duties.
The British Tradition
Modern boarding schools evolved significantly in Britain during the 16th to 19th centuries, producing generations of leaders, scholars, and military officers. Institutions like Eton, Harrow, and Rugby set a standard for discipline, academic excellence, and character formation.
Global Spread
Colonialism, globalization, and educational reform spread the boarding school model to countries like India, Australia, Africa, and the United States, where variations of the system adapted to local cultures and needs.
Types of Boarding Schools
Boarding schools today cater to a variety of students and educational philosophies:
1. Traditional Boarding Schools
These schools offer a broad curriculum and emphasize academic excellence, leadership, and tradition. Many are centuries old with strong alumni networks.
2. College-Preparatory Schools
Focused on preparing students for higher education, these schools emphasize rigorous academics, standardized test prep, and university counseling.
3. Military Boarding Schools
Designed to instill discipline, leadership, and physical fitness, military schools blend academics with structured daily routines and training.
4. Religious Boarding Schools
Affiliated with a religious institution or philosophy, these schools combine spiritual education with traditional subjects.
5. Performing Arts or Sports Schools
Specialized boarding schools focus on developing talents in music, dance, theater, or athletics, alongside academic learning.
6. Therapeutic Boarding Schools
These schools serve students with behavioral, emotional, or learning challenges, combining academics with counseling and therapy.
7. International Boarding Schools
Catering to a global student body, these schools often offer programs like the International Baccalaureate (IB) and promote cultural diversity.
Life Inside a Boarding School
1. Daily Routine
Boarding school life is highly structured. A typical day includes:
- Morning wake-up and breakfast
- Academic classes until afternoon
- Lunch and break time
- Extracurriculars (sports, arts, clubs)
- Dinner
- Evening study hours
- Lights out and curfew
This routine builds time management skills and fosters a sense of community.
2. Dorm Life
Students live in dormitories under the supervision of house parents or dorm masters. These adults provide emotional support, enforce rules, and serve as mentors.
Dorm life teaches independence, cooperation, hygiene, and social skills.
3. Extracurricular Opportunities
From robotics clubs and debate teams to rugby matches and theater productions, boarding schools provide a rich tapestry of co-curricular activities that develop well-rounded individuals.
Benefits of Boarding School Education
1. Academic Excellence
With longer school days, smaller class sizes, and highly qualified teachers, boarding schools often provide superior academic outcomes. Students benefit from focused learning and personalized attention.
2. Independence and Responsibility
Living away from home teaches students to manage their own schedules, handle daily chores, and make decisions—life skills that are invaluable in adulthood.
3. Community and Friendship
The tight-knit environment fosters strong bonds among students. Lifelong friendships, built through shared experiences, are common in boarding schools.
4. Cultural Exposure
Many boarding schools enroll students from various backgrounds and countries, encouraging cross-cultural understanding and global awareness.
5. Safe and Structured Environment
With round-the-clock supervision, zero tolerance policies for bullying, and controlled access to technology, boarding schools provide a safe and focused environment for growth.
6. Leadership Development
Students often take on roles such as dorm prefects, club presidents, or team captains—preparing them for future leadership in academic and professional settings.
Challenges of Boarding School Life
1. Homesickness
Living away from family can be emotionally difficult, especially for younger students. Boarding schools often have counselors and peer support systems in place.
2. Pressure to Perform
The high expectations in academics, sports, and leadership can lead to stress and anxiety. Time management and mental health support are crucial.
3. Cost
Boarding schools are often expensive, with tuition, boarding fees, and extras adding up. Scholarships and financial aid help make them accessible to diverse families.
4. Social Adjustments
Sharing space with peers of different habits, cultures, and personalities can be challenging—but also provides important social learning.
Boarding Schools vs. Day Schools: A Comparison
| Feature | Boarding School | Day School |
|---|---|---|
| Residence | Students live on campus | Students live at home |
| Supervision | 24/7 adult supervision | Supervised during school hours |
| Daily Schedule | Structured from morning till night | Flexible after school ends |
| Extracurriculars | Wide variety within school | Often outside school |
| Independence | High; self-care and planning | Limited; parental support available |
| Peer Interaction | Constant; deep bonds | Limited to school hours |
| Family Contact | Periodic visits, calls | Daily interaction |
| Cost | Generally higher | Usually more affordable |
Global Boarding School Models
United Kingdom
Renowned for historic institutions like Eton, Winchester, and Harrow, the UK boarding system emphasizes academic tradition, etiquette, and sportsmanship.
United States
Boarding schools like Phillips Exeter and Choate Rosemary Hall focus on college prep, liberal arts, and independent thinking.
India
Many boarding schools, like The Doon School or Mayo College, follow a blend of British traditions and Indian values, producing civic and business leaders.
Africa and Southeast Asia
In many developing nations, boarding schools provide access to education for rural populations. Some schools also double as safe havens from conflict or poverty.
Admission Process
Admission into a boarding school usually involves:
- Application form
- Entrance exam or standardized tests
- Interviews with the student and parents
- Letters of recommendation
- Academic transcripts
- Financial aid applications (if applicable)
Admissions teams look for academic ability, extracurricular engagement, and a willingness to adapt to communal life.
Boarding Schools in the Modern World
The concept of boarding school has evolved significantly in the 21st century. Today’s schools balance tradition with innovation:
1. Technology Integration
Smart classrooms, digital libraries, online collaboration tools, and learning management systems are becoming standard.
2. Mental Health Awareness
Schools now provide counseling services, wellness programs, and mindfulness training to support emotional well-being.
3. Sustainability Initiatives
Eco-conscious boarding schools incorporate solar energy, green buildings, and environmental education into their culture.
4. Career Readiness
Modern boarding schools focus not just on academics but also on entrepreneurship, coding, global citizenship, and internships.
Notable Alumni from Boarding Schools
Many leaders in politics, arts, and science have emerged from boarding schools:
- Prince William & Prince Harry – Eton College
- Jawaharlal Nehru – Harrow School
- Mark Zuckerberg – Phillips Exeter Academy
- Indira Gandhi – Swiss and Indian boarding schools
- Aung San Suu Kyi – St Hugh’s College, part of the Oxford system
These examples underscore how boarding schools can shape influential minds.
Is Boarding School the Right Choice?
Deciding to attend or send a child to boarding school is a significant decision. Here are key considerations:
- Is the student mature enough to live away from home?
- Does the school align with the child’s academic and personal interests?
- What kind of emotional and financial support is available?
- Is the school’s philosophy and structure suitable for the child’s personality?
Involving the child in the decision, visiting the campus, and discussing expectations can ensure a smoother transition.
Conclusion: A School, A Home, A Life Experience
Boarding schools offer more than just an education—they offer a lifestyle and a life experience. For many students, the years spent in a boarding school become the foundation for independence, lifelong friendships, critical thinking, and leadership.
While not suited for everyone, boarding schools can be a transformative journey for those who embrace their challenges and opportunities. As they continue to evolve with the times, these institutions remain relevant, respected, and revolutionary in the world of education.




⏱️ Xem giờ & bấm giờ nhanh với đồng hồ online — đếm ngược, bấm giờ, hẹn giờ, đồng hồ thế giới; chạy mượt trên điện thoại & PC, miễn phí, không cần cài đặt ⚡️🕒
يعد تطبيق البرامج. الاستفادة. جزء، التطبيق.
التطبيق، مساحة تخزين على جهازك. كذلك، جهوزية اتصالك. كان لديك، أثناء.
عند، يمكنك الشروع. يمكنك، بشكل سهل. الرابط، ستبدأ.
بعد الانتهاء من، تفعيل. قم بفتح. ثم، وإجراء.
Найдите идеальный вариант для своего бизнеса и slm 3d принтер купить|3д принтер slm купить|slm принтер по металлу купить|slm принтер купить уже сегодня!
Также можно посетить форумы, посвященные slm печати.
????????? ?? ????? ????? ??? ?????? ?? ????? . ?????? ??? ??????? ?? ???? ??????? ?????? ??????? . ??? ? ??? ?? ????? ?????? ???????? ???????? ???.
?? ???? ?????????? ???? ?????? ?? ?????. ??????? ?? ????? ???????? ???????? ?? ??????? ??????????? . ????? ??? ???????? ????? ?????? ???? ?? ?????.
?? ??????? ?? ???? ????? ????? ????? ?????????? ????????? ???? ?? ??? ????? ?????. ??? ???????? ??????? ??????? ??????? .
??????? ????? ???? ???????? ?? ???? ????, ????? ?? ????? ??????? ?????? ??. ???? ?? ???? ???????? ??? ?? ???? ?????? ???? ?????? ?????.
betfinal bahrain betfinal bahrain
slotul 100 super hot https://100-super-hots.com/ awaits you with exciting moments and the chance to win big!
Fashion this season is all about expressing oneself.
Discover a world of excitement and entertainment do fortune cookies come true!
True Fortune Casino is a popular destination for players looking for an exciting gaming experience. Offering a diverse selection of games, it caters to both casual players and high rollers. Including everything from slots to various table games, there is something for everyone.
Hello there, You’ve done an incredible job. I will certainly digg it and personally suggest to my friends. I’m sure they’ll be benefited from this web site.
escorts Rio
остров краби пхукет краби температура воды
Проект загородного дома Идеи для активного отдыха достаточно разнообразны и могут удовлетворить вкусы самых разных людей. Для тех, кто предпочитает активные развлечения, отличным вариантом станет организация спортивных мероприятий на свежем воздухе. Это могут быть как командные игры, такие как футбол или волейбол, так и индивидуальные занятия, например, йога на природе или утренняя пробежка по живописным маршрутам. Не забывайте о возможности организовать походы и велосипедные прогулки, которые подарят замечательные впечатления от общения с природой и позволят отвлечься от городской суеты.
https://bravomos.ru/ bravomos
онлайн работа дома для мам Находки ВБ для дома – это палитра возможностей для создания уютного гнездышка, отражающего ваш внутренний мир. От минималистичных скандинавских акцентов до роскошных элементов бохо, от умных гаджетов, облегчающих быт, до изысканных предметов декора, радующих глаз – каждый элемент призван наполнить пространство гармонией и функциональностью. Дилемма “находки ВБ или Озон” часто сводится к личным предпочтениям в навигации, ассортименте и программе лояльности, но beide платформы предлагают богатый выбор для обустройства дома.
Индексация пенсий Предпенсионер льготы – это права и привилегии, предоставляемые гражданам, находящимся в возрасте за несколько лет до выхода на пенсию. Эти льготы могут включать защиту от необоснованного увольнения, возможность пройти переобучение или повышение квалификации, а также получение различных социальных выплат и пособий. Поддержка предпенсионеров является важной задачей государства, направленной на обеспечение их трудовой занятости и социальной адаптации в период перехода к пенсионной жизни.
отражающая изоляция Армированная пленка – это усиленная версия полиэтиленовой пленки, обладающая повышенной прочностью и устойчивостью к разрывам. Благодаря армирующей сетке, интегрированной в структуру материала, армированная пленка способна выдерживать значительные нагрузки и противостоять механическим повреждениям. Ее используют в строительстве для создания временных укрытий, защиты фасадов зданий, а также в сельском хозяйстве для теплиц и парников, требующих повышенной надежности.
https://qwertyoop.com qwertyoop
https://opalubka.market/ opalubka market
sofa Мягкая мебель – это не просто предметы интерьера, это основа комфорта и уюта в вашем доме. Будь то удобный диван для вечернего отдыха, элегантная кровать для спокойного сна или стильное кресло для чтения любимой книги, правильно подобранная мягкая мебель способна преобразить любое пространство. Вы решили купить диван или обновить спальню новой кроватью? Отличная идея! Выбор мягкой мебели огромен, и важно найти именно то, что идеально впишется в ваш интерьер и будет соответствовать вашим потребностям.
https://kitehurghada.ru/ кайт школа хургада
бессмыслица дзен канал Полная ахинея и бессмыслица – для тех, кто хочет отвлечься от серьезного в Дзен!
Базы Xrumer 23 телеграм xrumer телеграм: xrumer телеграм – использование программного обеспечения Xrumer для продвижения Telegram-каналов и групп.
https://opalubka.market/ opalubka market
кайт школа эль-гуна горящие туры горя
Базы GSA телеграм xrumer официальный сайт телеграм: xrumer официальный сайт телеграм – упоминание официального сайта Xrumer в контексте продвижения в Telegram (прежде всего, канал разработчиков)
адвокат днепр Налоговый адвокат в Днепре: консультации по налоговому законодательству, защита при налоговых проверках, обжалование решений налоговых органов. Снижение налоговых рисков.
Базы GSA телеграм Прогон Xrumer телеграм: Прогон Xrumer телеграм – это услуга по продвижению Telegram-каналов и групп путем автоматического размещения ссылок на них на различных онлайн-платформах, используя Xrumer.
эвакуатор дешего Эвакуатор дешево Срочная эвакуация вашего автомобиля по самым выгодным ценам. Мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг эвакуации, от легковых автомобилей до мотоциклов и спецтехники. Наша команда профессионалов оперативно и аккуратно доставит ваш транспорт в любую точку города и области. Доступные цены и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту. Звоните прямо сейчас!
1win сайт Для новых пользователей предусмотрена простая и быстрая 1win регистрация. После ее завершения вы сможете пополнить счет и начать делать ставки или играть в казино.
атом казино официальный сайт Атом казино зеркало – это альтернативный способ доступа к сайту в случае блокировки основного домена. Используйте зеркало, чтобы не прерывать игру и продолжать наслаждаться азартом.
заказать проект каминопечи печи Купить проект каминопечи – объединить в одном устройстве функциональность печи и эстетику камина, создав неповторимый интерьер и источник тепла.
СПЕЙСЕР кольцо диэлектрическое Бордюры, Кольцо колодца, Колодцы кабельные ККС и Лоток водоотводной пластиковый – элементы благоустройства территории и строительства инженерных сетей.
заказать проект отопительной печи Купить проект отопительно-варочной печи – практичное решение для тех, кто ценит функциональность и желает иметь возможность готовить на традиционной печи.
атом казино бонусы Атом казино предлагает щедрые бонусы как новым, так и постоянным игрокам. Воспользуйтесь приветственным бонусом при регистрации и участвуйте в регулярных акциях для получения дополнительных призов и преимуществ.
Интерактивная панель Promethean в Алматы Как подключить интерактивную панель к ноутбуку: Простая инструкция. Подключение через HDMI, USB или беспроводную сеть.
AI seed phrase finder software Bitcoin wallet recovery tools hold promise, but their effectiveness often hinges on the degree of data loss and the user’s technical prowess.
Калибровка интерактивной доски в Алматы Крепление для интерактивной доски: Надежные кронштейны для монтажа на стену. Регулировка выноса проектора.
Интерактивная панель Promethean в Алматы Крепление для интерактивной доски: Надежные кронштейны для монтажа на стену. Регулировка выноса проектора.
как использовать бонусный счет на 1win в казино бонус
aonang paradise resort krabi краби Краби таун: столица провинции Краби.
краби таиланд обзор Краби Резорт: название отеля в Краби.
Обучение Xrumer телеграм xrumer официальный сайт: Официальный веб-сайт программного обеспечения Xrumer.
ко ланта ко ланте
где ко ланта ко ланта как добраться
расписание парома с пхукет на краби Ко Ланта Таиланд Отзывы: рай для тех, кто устал от суеты.
ко ланта ко ланте
страх
riobet Риобет Казино Вход: Быстрый Доступ к Вашим Любимым Играм Вход в Риобет казино осуществляется с помощью логина и пароля, указанных при регистрации. После входа вы можете сразу приступить к игре, пополнить счет или вывести выигрыш.
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию Бездепозитные Промокоды: Секретный Ключ к Эксклюзивным Бонусам Бездепозитные промокоды – это специальные коды, которые можно активировать в казино, чтобы получить эксклюзивный бездепозитный бонус.
риобет казино скачать Riobet: Совершенство в Каждой Детали Riobet – это не просто казино, это целый мир азарта и развлечений, где каждый игрок может почувствовать себя VIP-персоной.
занятия английским языком для детей
теория хаоса
юридическая помощь Банкротство – это сложный, но зачастую необходимый процесс для физических лиц, оказавшихся в тяжелой финансовой ситуации. Банкротство физических лиц позволяет гражданам, неспособным расплатиться по своим долгам, законно избавиться от долговых обязательств. Рефинансирование, в свою очередь, может стать альтернативой банкротству, позволяя снизить финансовую нагрузку путем изменения условий кредита. Ключевую роль в процедуре банкротства играет арбитражный управляющий, обеспечивающий соблюдение законности и защиту интересов всех сторон.
контракт в Твери Решение проблем, таких как долги или снятие ограничений ФССП, возможно через контракт. Работа для бывших военных и трудоустройство в армию по контракту также актуальны.
английский для школьников 17 лет
Адвокат Экибастуз Уголовный адвокат Казахстан: Защита по уголовным делам на любой стадии. Выезд в ИВС и СИЗО. Работаем 24/7 по всему Казахстану. Срочный выезд на задержание.
займы Процедура банкротства – это не увеселительная прогулка, а четкий юридический алгоритм, прописанный в законе о банкротстве. Банкротство через МФЦ – удобный упрощенный вариант, но доступен он далеко не всем. Долговые обязательства, как снежный ком, накапливаются и в итоге приводят к мысли об официальном банкротстве. Закон “о несостоятельности (банкротстве)” и “о банкротстве” – настольные книги для тех, кто решился на этот шаг. Отзывы о банкротстве – кладезь полезной информации, но не стоит забывать, что каждая ситуация индивидуальна.
https://nodepositcasino.ru Казино без депозита с выводом – это еще более привлекательная перспектива. Ведь возможность не только сыграть, но и вывести выигранные средства без предварительного пополнения счета звучит слишком заманчиво, чтобы быть правдой. Важно помнить, что такие предложения обычно сопряжены с определенными условиями и ограничениями, о которых следует узнать заранее.
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино без депозита
https://github.com/ciscosdk/Cisco-AnyConnect
римский электрический карниз Электрический карниз для штор – это больше, чем просто устройство. Это инвестиция в ваше удобство, в ваш комфорт, в ваш стиль жизни. Представьте себе: одним нажатием кнопки или голосовой командой вы создаете атмосферу уюта, регулируя естественное освещение в комнате, не вставая с дивана. Купить электрический карниз – значит сделать выбор в пользу инноваций и функциональности. Забудьте о неудобных шнурках и ручном управлении. Наслаждайтесь плавным и бесшумным движением штор, добавляя элегантности и современности вашему интерьеру.
https://enran.ua/
Ремонт в с. Туймебаев (Ащибулак). Гарантия на все виды работ.Ремонт стиральных машин Караой Надежный ремонт турецкой техники Beko. Устранение ошибок H1 (ТЭН), H7 (датчик). Замена нагревательных элементов Hi-Tech с никелевым покрытием и щеток двигателя. Доступные цены на запчасти и работу. Ремонт стиральных машин Atlant Алматы
vbet покер Vbet.am: Ваш надежный проводник в мир онлайн-развлечений
проститутки астана ?ыздар нет Астана: Горечь отказа, словно зимний ветер, пронизывает столичные улицы. В шумном мегаполисе, среди спешащих силуэтов и мерцающих огней, эти слова – крик о помощи, мольба об искренности. Это печальный рефрен, отражающий раны неразделенной любви и поиск настоящих чувств в мире фальши. Здесь каждый ищет свое место под солнцем, но многие тонут в одиночестве, не находя ответа на свой безмолвный вопрос.
эскорт Проститутки Алматы: За кулисами мегаполиса, где тени скрывают истории одиночества и отчаяния, расцветает темный цветок запретной страсти. Здесь, среди огней ночного города, продается не только тело, но и иллюзия близости, надежда на мимолетное счастье в объятиях незнакомца.
brazilian igaming summit
https://kadastr.msk.ru/styles/pgs/mediczinskie-ukladki-dlya-strojki-trebovaniya-okhrany-truda-2025.html
https://federalgaz.ru/
sigma eurasia
https://federalgaz.ru/
refurbished iPhone Europe
ликвидация Ozon Остатки Ozon и невыкупленные товары Ozon представляют собой большой потенциал для перепродажи. Эти товары, по разным причинам не дошедшие до конечного потребителя, могут быть реализованы с хорошей наценкой, особенно если правильно определить целевую аудиторию и разработать эффективную маркетинговую стратегию.
https://kotel-rs.ru/
https://kotel-rs.ru/
buy MacBook Air M2 Europe
https://kotel-rs.ru/
азино Азино сайт – это портал в мир виртуальных игр, где каждый может испытать свою удачу. Яркие баннеры, заманчивые предложения и бесконечный выбор развлечений – все это создает атмосферу, которая может легко увлечь. Важно помнить, что игра должна приносить удовольствие, а не создавать проблемы. Здравый смысл и умеренность – лучшие союзники в мире азарта.
azino Azino – это не просто набор букв, это символ, ставший частью онлайн-культуры. Его используют в рекламе, его упоминают в разговорах, он оставляет свой след в истории интернета. Однако, в погоне за прибылью и вниманием, важно помнить о моральных и этических принципах, не переступая черту дозволенного.
мелбет бонусы Мелбет промокод – это волшебный ключ, открывающий двери в мир увеличенных бонусов и более выгодных условий для ставок. Это возможность начать игру с преимуществом, увеличить свой первый депозит и получить фрибеты для тестирования различных стратегий. Промокод – это подарок, который дарит Мелбет своим новым и постоянным пользователям, позволяя им наслаждаться игрой в полной мере.
pokerok скачать Pokerok зеркало – это запасной вариант для доступа к платформе в случае блокировки основного сайта. Зеркало – это гарантия того, что игра не прервется ни при каких обстоятельствах, позволяя наслаждаться любимым развлечением в любое время и из любой точки мира.
melbet регистрации Melbet casino – это виртуальный рай для любителей азартных игр. Здесь собрана огромная коллекция слотов от ведущих мировых разработчиков, игры с живыми дилерами, рулетка, блэкджек и множество других развлечений. Melbet casino предлагает игрокам погрузиться в атмосферу настоящего казино, не выходя из дома. Высокое качество графики, честные выплаты и разнообразие игр делают Melbet casino одним из лучших онлайн-казино.
краби аэропорт онлайн сураттхани краби
https://vc.ru/migration/1171130-vnzh-ispanii-kak-poluchit-vizu-cifrovoi-kochevnik-ispanii-ili-digital-nomad-spisok-dokumentov-i-kakie-nalogi-platyat Не откладывайте свою мечту о жизни в Испании на потом. Обратитесь к нам прямо сейчас, и мы поможем вам осуществить ее быстро и эффективно. Мы гарантируем профессиональный подход, конфиденциальность и доступные цены. С нашей помощью вы сможете избежать лишних хлопот и сэкономить время и деньги. Мы делаем процесс получения ВНЖ Испании максимально простым и прозрачным.
https://evakuatorhelp.ru/ Не тратьте время на поиски других компаний, когда вам нужен надежный эвакуатор в СПб. Просто позвоните нам или оставьте заявку на сайте, и мы оперативно придем вам на помощь. Мы работаем 24 часа в сутки, 7 дней в неделю, без выходных и праздничных дней, чтобы вы могли быть уверены в нашей поддержке в любое время суток. Выбирайте профессионалов! Мы гарантируем высокое качество обслуживания и доступные цены. Наша репутация – это результат многолетней работы и сотен довольных клиентов.
сайт Мы понимаем, насколько стрессовой может быть ситуация, когда ваш автомобиль выходит из строя на дороге. Именно поэтому мы предлагаем круглосуточную поддержку и оперативный выезд эвакуатора в любой район Санкт-Петербурга. Наш парк спецтехники оснащен всем необходимым оборудованием для эвакуации автомобилей любого типа и размера, от малолитражек до внедорожников и микроавтобусов.
запчасти на автомобили Baw Помимо широкого ассортимента запчастей, мы предлагаем квалифицированную консультацию специалистов, готовых помочь в подборе необходимых деталей и предоставить техническую информацию. Мы понимаем, что правильный выбор запчасти – залог долговечной и безопасной эксплуатации автомобиля. Сотрудничая с нами, вы получаете не только качественную продукцию, но и надежного партнера, заинтересованного в вашем успехе. Выбирайте лучшее для своего китайского автомобиля!
https://vc.ru/migration/1335599-vse-vidy-vnzh-ispanii-kak-poluchit-spisok-dokumentov-i-trebovaniya-dlya-pereezda-na-pmzh-razberem-usloviya-i-osnovaniya-dlya-polucheniya-vida-na-zhitelstvo Наша команда экспертов всегда готова ответить на ваши вопросы и предоставить консультации по всем аспектам жизни и работы в Испании. Мы поможем вам разобраться в нюансах испанского законодательства, системы здравоохранения и образования. Мы предлагаем индивидуальные решения, учитывающие ваши личные обстоятельства и потребности.
покататься на слонах краби трансфер краби самуи
тут Наша команда экспертов всегда готова ответить на ваши вопросы и предоставить консультации по всем аспектам жизни и работы в Испании. Мы поможем вам разобраться в нюансах испанского законодательства, системы здравоохранения и образования. Мы предлагаем индивидуальные решения, учитывающие ваши личные обстоятельства и потребности.
аренда машин краби выездная церемония краби
Прогон Xrumer xrumer 23 strong ai телеграм
база xrumer телеграм Базы Xrumer 23 телеграм
Базы GSA Обучение Xrumer
остров ко ланта ко ланте
xrumer 23 strong ai телеграм xrumer 23 strong ai телеграм
Прогон Xrumer телеграм как работает xrumer 5.0 platinum
франшиза магазина фиксированных цен One Price https://oneprice.shop/
http://www.google.cv/url?q=http://oneprice.shop
УАЗ ПАТРИОТ АКПП УАЗ ПАТРИОТ с АКПП: Легендарный внедорожник, теперь с автоматической коробкой передач, предлагает беспрецедентный уровень комфорта и удобства управления. Забудьте о необходимости постоянно переключать передачи в сложных дорожных условиях. АКПП позволит вам полностью сосредоточиться на вождении и наслаждаться приключениями, будь то покорение бездорожья или комфортная поездка по городу. Просторный салон, вместительный багажник и мощный двигатель делают УАЗ ПАТРИОТ с АКПП идеальным выбором для тех, кто ценит свободу передвижения и не боится вызовов природы. Этот автомобиль станет вашим надежным спутником в любых путешествиях и поможет справиться с любыми задачами, которые поставит перед вами жизнь. Откройте для себя новые возможности с УАЗ ПАТРИОТ АКПП!
УАЗ ПАТРИОТ АКПП УАЗ ПАТРИОТ с АКПП: Это не просто внедорожник, это легенда, адаптированная к современным требованиям комфорта и управляемости. Автоматическая коробка передач, которой оснащен этот автомобиль, значительно упрощает процесс вождения, особенно в сложных условиях бездорожья и городского трафика. Представьте себе: вы легко преодолеваете любые препятствия, не отвлекаясь на постоянное переключение передач, а просто наслаждаетесь поездкой. Просторный салон, вместительный багажник, высокий клиренс и мощный двигатель делают УАЗ ПАТРИОТ с АКПП идеальным выбором для тех, кто ценит свободу передвижения и не боится выезжать за пределы асфальтированных дорог. От рыбалки и охоты до семейных путешествий и экстремальных приключений – этот автомобиль справится с любыми задачами. Не упустите возможность стать обладателем надежного и универсального внедорожника, который подарит вам незабываемые впечатления!
прогнозы на футбол Прогнозы на хоккей: будь в курсе всех событий и делай выигрышные ставки!
оргонная_подвеска Биоамулеты: Амулеты для биоэнергетики.
Купить ПВХ окна в Алматы Выбор качественных пластиковых окон – это инвестиция в комфорт, тепло и энергоэффективность вашего дома. В Алматы, в условиях переменчивого климата, это особенно актуально. Компания Okna Service предлагает широкий ассортимент пластиковых окон, отвечающих самым высоким стандартам качества. Okna Service использует только проверенные профильные системы от ведущих производителей. Это гарантирует долговечность, устойчивость к перепадам температур и отличную звукоизоляцию. Вы можете выбрать окна с различной толщиной профиля, количеством камер и типами стеклопакетов, в зависимости от ваших индивидуальных потребностей и бюджета. Помимо качества продукции, Okna Service выделяется своим профессиональным подходом к установке. Квалифицированные монтажники с большим опытом работы гарантируют правильную установку окон, что является критически важным для обеспечения их функциональности и долговечности. Неправильный монтаж может свести на нет все преимущества даже самых дорогих окон. Okna Service предлагает полный спектр услуг, включая замер, изготовление, доставку и установку окон. Компания также предоставляет гарантийное и постгарантийное обслуживание. Вам помогут подобрать оптимальное решение для вашего дома или офиса, учитывая особенности архитектуры и ваши личные пожелания. Выбирая Okna Service, вы выбираете надежность, качество и профессионализм. Улучшите свой дом уже сегодня, установив новые пластиковые окна от Okna Service.
Пластиковые окна в Алматы цена Выбор качественных пластиковых окон – это инвестиция в комфорт, тепло и энергоэффективность вашего дома. В Алматы, в условиях переменчивого климата, это особенно актуально. Компания Okna Service предлагает широкий ассортимент пластиковых окон, отвечающих самым высоким стандартам качества. Okna Service использует только проверенные профильные системы от ведущих производителей. Это гарантирует долговечность, устойчивость к перепадам температур и отличную звукоизоляцию. Вы можете выбрать окна с различной толщиной профиля, количеством камер и типами стеклопакетов, в зависимости от ваших индивидуальных потребностей и бюджета. Помимо качества продукции, Okna Service выделяется своим профессиональным подходом к установке. Квалифицированные монтажники с большим опытом работы гарантируют правильную установку окон, что является критически важным для обеспечения их функциональности и долговечности. Неправильный монтаж может свести на нет все преимущества даже самых дорогих окон. Okna Service предлагает полный спектр услуг, включая замер, изготовление, доставку и установку окон. Компания также предоставляет гарантийное и постгарантийное обслуживание. Вам помогут подобрать оптимальное решение для вашего дома или офиса, учитывая особенности архитектуры и ваши личные пожелания. Выбирая Okna Service, вы выбираете надежность, качество и профессионализм. Улучшите свой дом уже сегодня, установив новые пластиковые окна от Okna Service.
мужской_амулет Кулонженский: Украшене на на шею для женщины.
Мир онлайн-слотов растёт: новые провайдеры, повышенные RTP и постоянные турниры поддерживают интерес игроков.
Vavada удерживает позиции в топе, но не забывайте проверять лицензию и лимиты перед депозитом.
Выбирайте автоматы с бонусными раундами, бесплатными вращениями и прогрессивными джекпотами — так повышается шанс крупного выигрыша.
Зеркала решают проблему блокировок и позволяют оперативно выводить средства без лишних задержек.
Актуальные возможности доступны здесь: http://global-climate-change.ru/media/pgs/v_kakom_kazino_daut_realnue_dengi_za_registraciu__9.html.
Играйте ответственно и контролируйте банкролл, чтобы азарт оставался в пределах удовольствия.